Mitosis is the process, in the cell cycle, by which the chromosomes in the cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis is followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane, and later karyokinesis, which divides the nucleus, dividing the cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components
There are six phases of mitosis. Each phase is used to describe what
kind of change the cell is going through. The phases are interphase,
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Some may
consider pro-metaphase as part of the phases but most believe it is part
of metaphase and some of prophase. Each phase is important to mitosis.
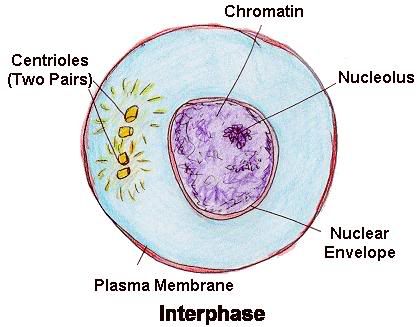
Interphase
The chromosomes cannot be seen but they duplicate the DNA and double in mass when it starts to copy its own DNA.
Prophase
During prophase, chromosomes in the nucleus condense, pairs of centrioles move
to opposite sides of the nucleus, spindle fibers form a bridge between
the ends of the cell, the nuclear envelope breaks down and the nucleus
begins to disappear.
Metaphase
During metaphase, the chromosomes are pulled by microtubules called spindle fibers into place. The chromosomes line up on the cell's equator, or center line, and are prepared for division.
Anaphase
During anaphase the chromosomes move from the cell's equator (metaphase
plate) to their respective poles of the cell. The cell begins to stretch
out as the opposite ends are pushed apart.
Telophase
Telophase is the final stage in mitosis, as the cell itself is ready to
divide. One complete set of chromosomes is now at each pole of the cell.
The spindle fibers begin to disappear, and a nuclear membrane forms
around each set of chromosomes. Also a nucleolus appears within each new nucleus and single stranded chromosomes uncoil into invisible strands of chromatin.
You didnt understand?
You didnt understand?
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario